In Southwest Florida, where hurricane season brings unpredictable weather and frequent power outages, having a reliable power backup system is crucial for homeowners. One of the most effective ways to ensure your home is always powered, regardless of external conditions, is by installing a generator during the construction phase of your new home.
The Benefits of Installing a Generator During Construction
A generator can keep your home powered during extreme conditions and ensure the comfort and safety of your family and pets. Adding a generator and fuel tank while your home is under construction offers several benefits:
- Seamless integration into your home’s design allows for optimal placement of fuel tanks, gas lines, and electrical connections, making the system a natural part of your home.
- Avoids the hassle of retrofitting by installing the generator during construction, preventing the extra costs and effort associated with modifying your home later.
- Eliminates wall cutting and utility rerouting that comes with retrofitting, preserving your home’s structure and saving you from future disruptions.
- Ensures efficient installation from the start, aligning the generator system with your home’s original plans, which reduces potential complications down the line.
How Generators Hook into Homes
Installing a generator for your home is a complex process that involves careful planning, professional installation, and a thorough understanding of electrical systems. Here’s a breakdown of how a generator is integrated into a new home:
- The Generator Itself
The heart of the system is the generator unit. Depending on the package you choose, it could be a portable unit for partial home coverage or a standby generator for whole-home power. The generator is typically placed outside the home, at least 18 inches away from the structure and 5 feet from any operable windows or doors, to meet safety requirements.
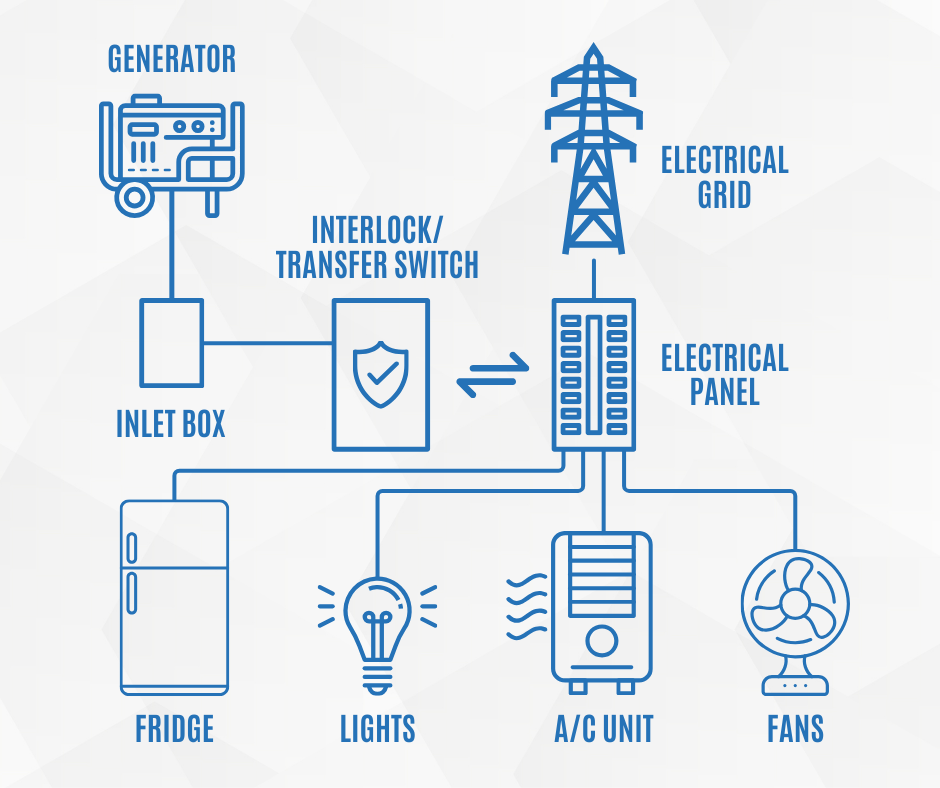
- Electrical Panel Integration
The generator, whether portable or standby, is hooked into the home’s electrical panel through the transfer switch. The electrical panel is divided into circuits, which control different parts of the home, such as lighting, HVAC, appliances, etc. Depending on your generator’s capacity, certain circuits will be prioritized. For instance:
- Portable Generators: Can typically handle lights, refrigerators, small appliances, and some fans.
- Standby Generators: These can be hooked up to power the entire house, including air conditioning and multiple appliances, depending on the generator’s wattage.
- Interlocking Kit for Portable Generators
If you opt for a portable generator, an interlocking kit is used to safely connect the generator to your home’s electrical panel. This system prevents backfeeding—when electricity flows in the wrong direction and poses a danger to utility workers or neighbors—and ensures that only selected circuits in the home are powered. You’ll also have an inlet box on the exterior of your home where you can plug in the generator during an outage.
- Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) for Standby Generators
For standby generators, an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) is essential. This device constantly monitors the power supply from the utility company. If the ATS detects a power outage, it automatically switches the electrical load of your home to the generator. This ensures that the power seamlessly switches to backup mode without you having to manually start the generator or connect it to your home.
In the case of whole-home systems, every circuit in the home is powered as if there were no outage at all.
Fuel Supply Connection
A reliable fuel supply is the best method of ensuring your generator runs smoothly during power outages. Our standby generators typically run on propane, and optional fuel systems can be connected to ensure seamless operation. Here’s how it works:
- Above-Ground and Buried Propane Tanks: Depending on your propane needs, you can choose between different tank sizes, from 125-gallon above-ground tanks to 500-gallon buried tanks. These tanks store the fuel needed to power the generator and are installed with safety clearances to ensure compliance with Florida’s regulations.
- Above-Ground Tanks: Must be placed at least 10 feet from ignition sources and 5 feet from windows or doors.
- Buried Tanks: Must be 10 feet from ignition sources, buildings, and property lines. Both types must avoid utility easements to meet safety regulations.
- Gas Lines and Tubing: The fuel supply is connected to the generator via underground gas lines (for buried tanks) or corrugated stainless steel tubing (CSST) (for above-ground tanks). These lines ensure a steady and reliable flow of fuel from the tank to the generator, enabling it to run continuously during an outage without needing manual refueling.
- Automated Fuel Flow: Once installed, the system works automatically. The fuel tank provides a constant supply of propane to the generator, ensuring that it’s ready to power your home whenever an outage occurs. With standby generators, this system operates without any manual intervention, making it a hassle-free backup power solution for your home.
This seamless integration of the fuel supply into the generator setup ensures that your home is prepared for extended power outages without the need for frequent refueling or manual oversight.
Learn About Our Generator Packages
There’s no better time to invest in a generator and fuel tank than during your home’s construction. Our team can help you choose the best package for your needs and ensure that it is installed seamlessly. If you’re interested in learning more about our generator packages or want to discuss adding this feature to your new home, contact us today.